- Impact of process conditions
- All eyes on the retention rate
- Various design principles
- String-wound depth filter cartridges
- Activated carbon filter cartridges
- Melt-blown depth filter cartridges
- Pleated filter cartridges
- Membrane filter cartridges
- Metal filter cartridges
Whether in wastewater treatment, chemical production or microchip factories: Filtration is a fundamental process in solid liquid separation. Due to their versatility, simple yet robust structure, high reliability and relatively low costs filter cartridges are now indispensable here. Different versions are available to suit their diverse range of applications. This means that even critical filtration requirements that call for a high and consistent retention efficiency of the filter medium can be met. When choosing the right filter cartridge, users need to consider various aspects to achieve the optimal level of performance. Some of the most important criteria include:
- Operating principles of the filters
- Process conditions such as flow rate, pressure, temperature and dynamic viscosity
- Retention rate of the filter material and size of particles to be removed
- Design principals and components
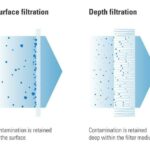
From a technical point of view, filter cartridges are differentiated according to two filtration principles: surface filtration and depth filtration. With surface filtration, particles and solids are retained on the surface, while with depth filtration, particles are retained deep within the filter medium.
Impact of process conditions
The retention rates of filter cartridges can range from approx. 250 down to 0.03 µm. Process conditions during filtration can have a significant impact on the performance of filter cartridges, as shown by the following examples.
- Operating pressure determines the thickness of the filter housing shell, among other things
- Operating temperature determines the housing material (stainless steel or plastic)
- Volume flow determines the size of the housing
- Dynamic viscosity has a direct effect on the differential pressure (and therefore also on the size of the housing)
- Chemical compatibility has a direct effect on the choice of housing material (a coating may be required)
The shape, concentration and composition of the particles also play an important role when selecting the suitable filter medium. Chemical and thermal compatibility also must not be overlooked.
All eyes on the retention rate
Another important aspect to differentiate filter cartridges is the retention rate. The retention rate is specified as either absolute or nominal and has a direct effect on the filtration result. The reason: Filtration of a liquid may require only specific contaminants to be removed, while others that are not critical to the process or that are even valuable to the product may or must remain in the filtrate.
If all particles of a specified size need to be removed, a filter cartridge with an absolute retention rate is required. The absolute retention rate indicates the pore size of the filter medium. All particles that do not fit through the pores are reliably retained according to a retention efficiency defined under laboratory conditions. For example, an absolute retention rate of 10 μm means that particles at least 10 μm in size are retained after being passed through the filter cartridge once. If 5000 of these particles are measured in the liquid before filtration and only one particle is measured in the filtrate after filtration, the filter cartridge has achieved a beta ratio of 5000. This corresponds to a retention efficiency of 99.98 %.
A nominal retention rate, on the other hand, refers to a filter cartridge that retains an undefined percentage of solid particles that are larger than the specified pore size.
Various design principles
The size of the filter cartridge determines the size of the filter surface. To maximise the size of the filter surface, the filter material can be pleated by folding the filter media sheets like a harmonica. The exception to this are melt-blown depth filter cartridges.
To provide the right filter cartridge for every application, cartridges are available in different diameters and lengths. For example, the outer diameter of the typical and frequently used size is between 60 and 72 mm (2.4 and 2.8″). Standard lengths vary from 127 to 1778 mm (5 to 70″). A range of different adapters allow the filter cartridge to be installed in different style housing types. Common adapter designs are the Double Open End (DOE) version, open on both sides and Single Open End (SOE) version, open on one side . The flow direction of filter cartridges is usually from the outside inward.
String-wound depth filter cartridges
String-wound filter cartridges are depth filter media made of staple fibers, which are suitable for separating contaminants with a wide range of particle sizes (clarification). These proven filter cartridges also boast a high dirt-holding capacity and a long service life. Originally, these filter cartridges were made from cotton. Today there are also alternatives made from polypropylene, fiberglass, polyamide, polyester and polyphenylene sulfide. The inner cores are usually made from polypropylene or stainless steel. They are typically used for the filtration of process chemicals, solvents, galvanic baths, acids, alkalis, process water and for the desalination of sea water.
Activated carbon filter cartridges
These filter cartridges are available in different designs: One design is granular activated carbon in a porous polyethylene cage with polypropylene end caps and a particulate pre-filter. The other design is sintered activated carbon blocks with a particulate pre-filter made from a polypropylene net or fleece and corresponding end caps. Activated carbon filter cartridges are used for the filtration of process water, water-based and organic solutions and for removing organic contaminants from galvanic nickel or copper baths.
Melt-blown depth filter cartridges
These filter cartridges are made from pure polymers, meaning they are suitable for separating contaminants with a wide range of particle sizes as well as removing all particles of a specified pore size (classification). They are available with nominal retention efficiencies of 80 to 95 % and with an absolute retention efficiency of 99.98 %. Standard filter materials include polypropylene, polyamide and polyester. They can be used for a wide range of applications, including filtration of ultra-pure water, acids, alkalis, emulsions, e-coating (electro-coating in automotive), solvents, amines, glycols, hydrocarbons (kerosene), water- and solvent-based paints, lacquers, emulsions, waxes and condensates.
Pleated filter cartridges
Pleated filter cartridges have a large filter surface of approx. 0.5 to 0.7 m² per 10″ element (254 mm), which enables high flow rates with low initial differential pressure. Filter materials include polypropylene, fiberglass, polyamide and polyester.
High flow filter cartridges also belong to this group and can be used to handle particularly high volume flows. However, they differ not only in terms of their outer diameter, which is approximately 152 or 165 mm (6 or 6.5″), but also in terms of their flow direction, which unlike most other filter cartridges is from the inside outward. Pleated filter cartridges are used in the filtration of process water, wastewater, chemicals and inks, for cleaning parts and for pre-filtration in reverse osmosis for ultra-pure water.
Membrane filter cartridges
The pleated filter surface of the membrane filter cartridges ranges from approx. 0.5 to 0.9 m² per 10″ element. Depending on the application, a range of different filter materials are available: Polyethersulfone, polysulfone, polyamide 6.6 and polytetrafluoroethylene among others. Applications are usually linked to the requirement for filtration according to absolute retention rates.
Metal filter cartridges
In the case of metal filter cartridges, the filter material is usually made from stainless steel in a cylindrical or pleated wire mesh structure. They are also available in a sintered design, for example with titanium filter material. They are especially suitable for applications with very high temperatures of up to 370 °C and for the filtration of corrosive liquids and gases, cryogenic fluids, high-viscosity solutions, process steam and for catalyst recovery.
Determining which filter cartridge is suitable for which application depends on process parameters, the required performance and economic factors. For operators who need efficient filtration, it is therefore worth taking a closer look at the available options. Eaton‘s Filtration Division provides partners and customers with comprehensive guidance for selecting the right filtration system and provides the same high-quality products worldwide. When it comes to designing the right filtration system for the application, expertise always pays off.
Eaton Technologies, Filtation Solutions