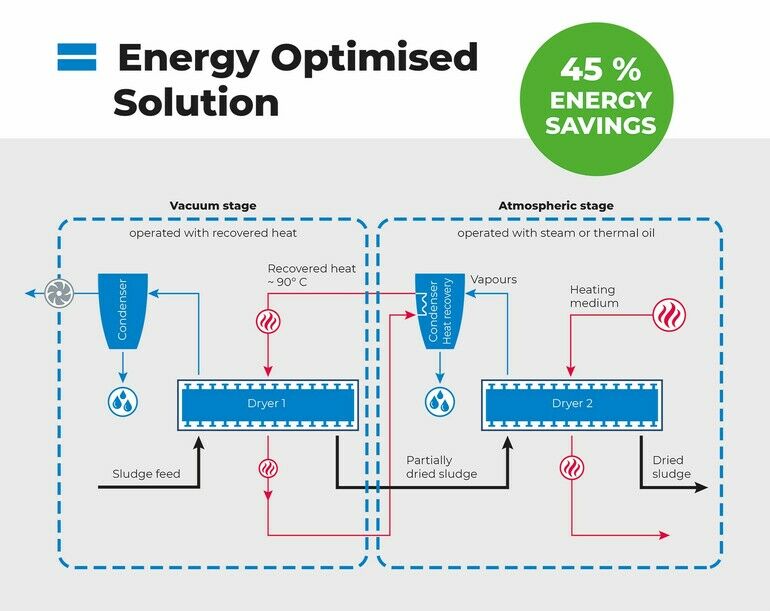
Buss-SMS-Canzler‘s two-stage drying process can be used for a variety of applications, including the drying of sewage sludge. The thin-fiilm evaporation system is designed to reduce heating-energy consumption by 45% compared to conventional sludge-drying equipment.
Traditional drying techniques often require a substantial amount of energy input, mainly due to the limited utilization of heating energy. The two-stage drying process capitalizes on the principle of multiple-effect evaporation commonly used in evaporation technology. Multiple-effect evaporation is designed to maximize the use of input energy. By operating under vacuum conditions in Stage 1 and atmospheric conditions in Stage 2, this process enables a lower evaporation temperature in stage 1, resulting in considerable energy savings, according to the company.
One of the key advantages of the design is the recovery of energy released during the condensation in stage 2. This energy is then utilized to heat stage 1 (see diagram). The two-stage drying process efficiently applies products in a thin film on the heated wall using rotating blades. This approach not only enhances the effectiveness of the drying process, but also makes it suitable for various applications, including the drying of sewage sludge. The dried sludge would be suitable for a variety of uses, including gasification, composting, incineration, fertilizer, pyrolysis and others.
Buss-SMS-Canzler
Achema: Hall 4.0, Stand B24